Comprehensive Guide to Uterine Fibroids Treatment at Laser Stone Hospital in Rohini
Understanding Uterine Fibroids
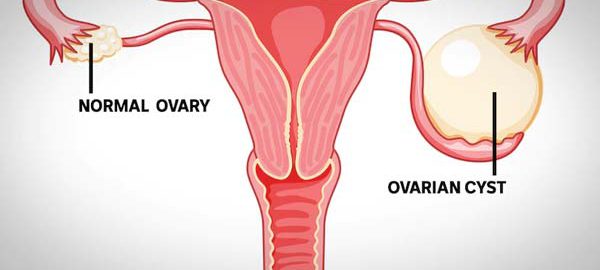
Uterine fibroids, also known as leiomyomas or myomas, are non-cancerous growths that develop in or on the uterus. These benign tumors are composed of smooth muscle cells and fibrous connective tissue. Although the exact cause of uterine fibroids remains unclear, factors such as hormonal imbalances, genetic predispositions, and environmental influences are believed to play significant roles.
There are several types of uterine fibroids, categorized based on their location within the uterus. Intramural fibroids are the most common, found within the muscular wall of the uterus. Subserosal fibroids extend beyond the uterine wall into the pelvic cavity, while submucosal fibroids develop underneath the uterine lining and can protrude into the uterine cavity. Additionally, pedunculated fibroids grow on a stalk either outside or inside the uterus.
Fibroids can significantly impact a woman’s health and quality of life. Common symptoms include heavy menstrual bleeding, prolonged periods, pelvic pain, frequent urination, constipation, and backache. Some women may also experience reproductive issues such as infertility, recurrent miscarriages, or complications during pregnancy and labor.
Several risk factors are associated with the development of uterine fibroids. These include age, with women in their 30s and 40s being most commonly affected, and ethnicity, as African American women are more likely to develop fibroids than women of other ethnicities. Other risk factors include obesity, a family history of fibroids, early onset of menstruation, and a diet high in red meat and low in green vegetables, fruits, and dairy.
Statistical data indicate that up to 70% of women will develop fibroids by the age of 50, with a higher prevalence observed in African American women compared to Caucasian women. Understanding these risk factors and symptoms is crucial for early detection and effective management of uterine fibroids.
Diagnostic Procedures for Uterine Fibroids
Detecting uterine fibroids accurately is critical for effective treatment. Various diagnostic procedures are employed to identify the presence, size, and location of fibroids. Among these, imaging techniques such as ultrasound, MRI, and CT scans play a pivotal role.
Ultrasound is often the first step in the diagnostic process. This non-invasive technique utilizes high-frequency sound waves to create detailed images of the uterus. A transvaginal ultrasound, where the probe is inserted into the vagina, provides a closer and more precise view of fibroids compared to an abdominal ultrasound. Ultrasound imaging is particularly useful due to its accessibility and cost-effectiveness.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) offers a more comprehensive view of fibroids, especially in cases where ultrasound results are inconclusive. MRI uses strong magnets and radio waves to produce high-resolution images of the uterus and surrounding structures. This technique is beneficial for mapping fibroids before surgical interventions and for differentiating fibroids from other pelvic masses.
Computed Tomography (CT) scans, though less commonly used for fibroid detection, can still provide valuable information. CT scans combine X-ray images taken from different angles to create cross-sectional images of the body. This method is particularly useful in complex cases where detailed anatomical information is required.
In addition to imaging techniques, other diagnostic tools such as hysteroscopy and laparoscopy are employed. Hysteroscopy involves the insertion of a thin, lighted tube through the cervix into the uterus, allowing direct visualization of the uterine cavity. This procedure is particularly effective in diagnosing submucosal fibroids. Laparoscopy, on the other hand, involves making small incisions in the abdomen to insert a camera, providing a clear view of the outer surface of the uterus and other pelvic organs.
Early detection through routine gynecological exams is crucial in managing fibroid-related health issues. Regular pelvic exams can help in identifying fibroids before they cause significant symptoms or complications. Early diagnosis allows for a wider range of treatment options, potentially preventing the need for more invasive procedures.
Treatment Options for Uterine Fibroids at Laser Stone Hospital
Laser Stone Hospital in Rohini offers a comprehensive range of treatments for uterine fibroids, catering to various patient needs and medical conditions. The hospital’s multidisciplinary approach ensures that each patient receives personalized care, starting with a thorough diagnosis to determine the most suitable treatment plan. Among the non-surgical treatment options are medication and hormonal therapy, which aim to manage symptoms and reduce the size of fibroids.
Medications primarily include Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists, which help shrink fibroids by lowering estrogen and progesterone levels. Other medications, such as anti-inflammatory drugs, can alleviate pain and heavy menstrual bleeding, while oral contraceptives may regulate menstrual cycles and reduce symptoms. Hormonal therapy, involving progestin-releasing intrauterine devices (IUDs), can also be effective in controlling excessive bleeding and fibroid growth.
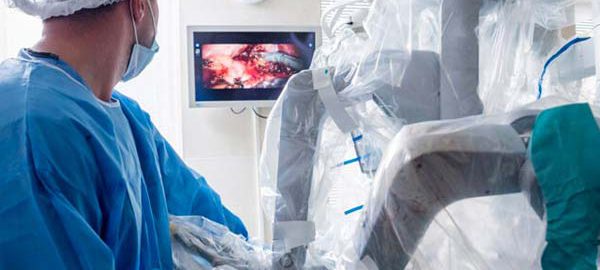
For patients requiring surgical intervention, Laser Stone Hospital is equipped with advanced technologies to perform minimally invasive procedures. Uterine artery embolization (UAE) is a notable method, where tiny particles are injected into the uterine arteries to block blood flow to the fibroids, causing them to shrink. This procedure is particularly beneficial for those seeking a quicker recovery and fewer complications compared to traditional surgery.
Laparoscopic myomectomy is another minimally invasive surgical option available at the hospital. This procedure involves the removal of fibroids through small incisions in the abdomen, preserving the uterus and offering a shorter recovery period. The use of laparoscopic techniques ensures minimal scarring and reduced post-operative pain, making it a preferred choice for many patients.
A distinctive feature of Laser Stone Hospital is its utilization of advanced laser technology for fibroid removal. This innovative approach allows for precise targeting of fibroids, minimizing damage to surrounding tissues and enhancing the overall success rates of the procedures. The benefits of laser treatments include shorter hospital stays, quicker recovery times, and a significant reduction in the risk of complications.
Patient Care and Support Services at Laser Stone Hospital
At Laser Stone Hospital in Rohini, patient care and support services are of utmost importance. The hospital ensures that every patient receives comprehensive care starting from the initial consultation to post-treatment follow-up. During the pre-treatment consultations, patients undergo thorough evaluations by specialized medical professionals. These consultations are designed to understand the patient’s medical history, current health status, and specific needs, allowing the development of personalized treatment plans tailored to each individual’s condition.
Once a treatment plan is established, patients are guided through every step of their journey. The hospital’s staff is dedicated to providing a supportive and compassionate environment, ensuring that patients feel comfortable and informed throughout their treatment. Post-treatment follow-up care is an integral part of the patient care protocol at Laser Stone Hospital. Regular check-ups and monitoring ensure that patients are recovering well and that any potential complications are addressed promptly.
The hospital takes pride in its patient testimonials and success stories, which highlight the exceptional care and positive outcomes experienced by many. These testimonials reflect the hospital’s commitment to patient well-being and satisfaction. By sharing these success stories, Laser Stone Hospital aims to provide reassurance and hope to those undergoing treatment for uterine fibroids.
For those looking to book an appointment, the hospital offers a straightforward process. Appointments can be scheduled through their website or by contacting the hospital directly. Additionally, Laser Stone Hospital understands the financial concerns that may arise with medical treatments. Therefore, they provide information on insurance coverage and offer financial assistance options to ensure that patients have access to the necessary care without undue financial burden.
In summary, Laser Stone Hospital’s dedication to patient care and support services underscores their commitment to delivering high-quality medical treatment and ensuring patient satisfaction. From personalized treatment plans to compassionate follow-up care, the hospital strives to make every patient’s journey as smooth and successful as possible.